What is the definition of electric wire? What is the difference between an electric wire and an power cable?
What is the definition of electric wire? What is the difference between an electric wire and an power cable?
Wires are one or more string metal strands, 99% of which are made of copper metal and are protected by a plastic sheath called insulation. In today's world of modern technology, wires are one of the most widely used materials in the world. It is used around us in commercial, office and construction buildings, systems, machines, various industrial machines and thousands of other things. One of the most widely used cases of wires is in the electricity industry.
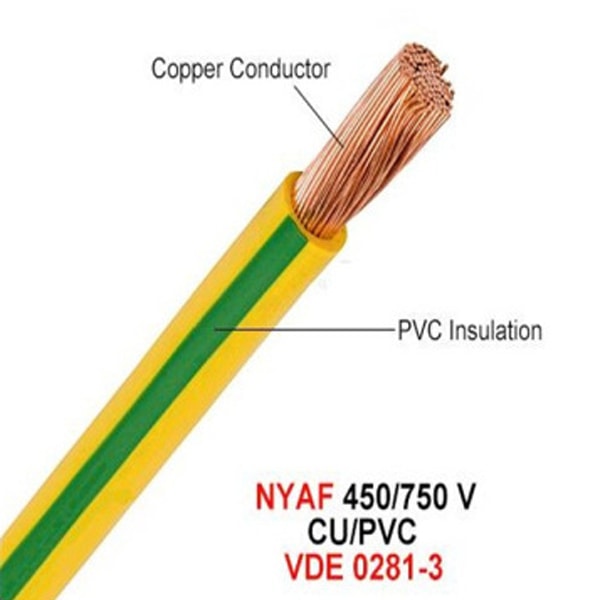
Wire is used to transfer electrical current from one point to another. Energy transmission in wires, like other similar products, is done by the internal part called the conductor. The conductor is the part of the electric wire that is responsible for transmitting electricity. Also, layers of polymer are placed on the conductor to prevent the conduction of electricity. This layer, which is called "insulation", is responsible for preventing the conduction of electric current.
The electrical wires in the power industry are introduced as follows in terms of production structure and type of conductor used in it:
1- conductor Single-stranded or electric wire or wired electric wire (NYA)
2- Electric wire or multi-threaded conductor or NYAF
3- Electric wire or multi-threaded conductor, regular or semi-spray Electric wire
 What is a Electric wire?
What is a Electric wire?
To transmit electrical potential from one point to another, electrical wires that conduct electricity are used. The Electric wire is usually made of an electrical conductor and an electrical insulator that is coated on the conductor. Electric wire conductors are usually made of copper or aluminum or their compounds. Copper conduction is better than aluminum. So copper wires perform better, although they are more expensive. Electrical wire insulation is a plastic material whose job is to provide electrical insulation of the wire with electrical potential from its surroundings. Depending on its application, electrical wires are available in a variety of thicknesses and shapes.
 What is the classification of electric wires in the
electricity industry in terms of production structure and
the type of conductor used in it?
What is the classification of electric wires in the
electricity industry in terms of production structure and
the type of conductor used in it?
Electrical wires in the power industry are classified as follows in terms of production structure and type of conductor used in it.
1- Electric wire or multi-threaded conductor or(NYAF) .
2- Electric wire or multi-threaded conductor, regular or semi-spray Electric wire.
3-- conductor Single-stranded or electric wire or wired electric wire (NYA).
The use of these three models of electric wire is used depending on the place of use and the environmental conditions and the type of project, etc., and the amount of current that is to pass through the conductor used in the electric wire.
 What is electric wire numbering? What is the name of the
electric wire?
What is electric wire numbering? What is the name of the
electric wire?
To use wires in different places, it should be noted that the wires are numbered based on the thickness of the copper used in them and are used in different places. These numbers are generally as follows:
5/. - 75/. - 1 - 5/1 - 5/2 - ۴ - ۶ - ۱۰ - ۱۶ - ۲۵ - ۳۵ - ۵۰ - ۷۰ - ۹۵ - ۱۲۰ - ۱۵۰ - ۱۸۵ - ۲۴۰ - ۳۰۰ - ۴۰۰ – ۵۰۰
Also, wires in the electrical industry are known by specific names that are defined as standard. These names are:
NYAF wire and NYA wire and NYIF wire under gypsum and Y wire with a score of 0.75 for news alarm as well as G wire with rubber cover and F wire for wet space and T wire are for dry space.
 What are the components of an electric wire?
What are the components of an electric wire?
A wire has two parts:
1- electric wire conductor:
The part that is the core of the wire is called the conductor, which should be selected according to the different voltages and currents according to the high numbering and in consultation with experts.
2- Sheath (insulation) or Electric wire cover:
The part of the brain that encloses and protects the conductor, as well as the external contact of the conductor, insulates the electric wire Or they call it electric wire coating.
Basically, electrical insulation material is made of plastic or PVC.
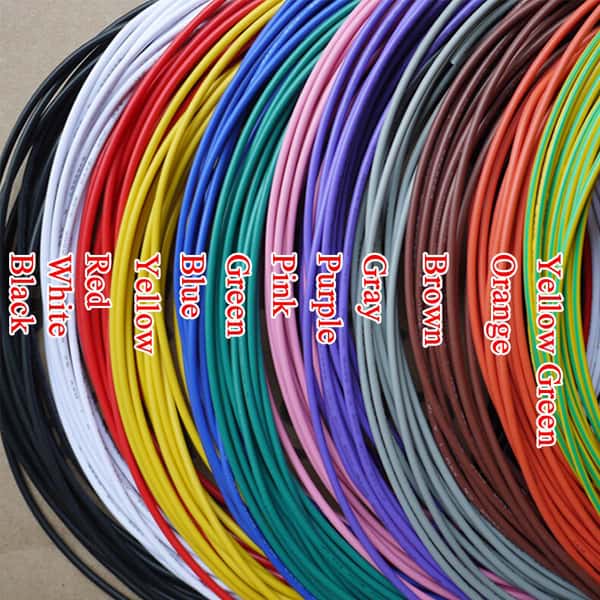
 What is the importance of color in electrical wiring and
according to what principles is it explained?
What is the importance of color in electrical wiring and
according to what principles is it explained?
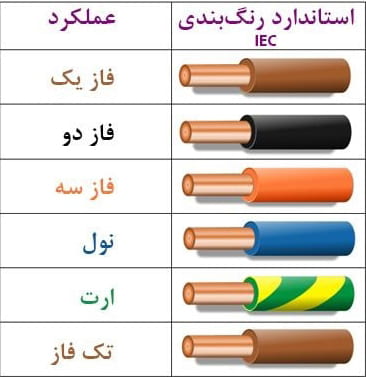
To use a electric wire, for example, in a building unit, there are basically three models of conductors:
1- Phase conductor.
2- Neutral conductor.
3- protection system ground or earth conductor.
 What is a phase wire or a phase conductor?
What is a phase wire or a phase conductor?
Phase wire can be considered the most dangerous wire in a building's electrical circuit. Because the phase wire carries the electric charge and transmits its electric charge to them as soon as it comes in contact with the conductive components, the phase is also called the current-carrying wire. The phase is usually detectable by black insulation. Of course, to display phase wire other than black, any color other than white, green, gray, and blue is used. In power plants, three wires supply power to the consumer. These three power wires are similar. But their voltage is phase different. The implication of this sentence is that these three wires have a potential difference, so as we have said before, if we connect two of them to the two ends of one device, that device will light up. The three-phase motor works in the same way. Each of these wires is called a single-phase power supply. The potential difference between each of these wires is very high. For example, the potential difference between each wire in an out-of-town power supply system is 2,000 volts. These four wires consist of three phases and a neutral. Each phase has a potential difference of 380 volts relative to each other and each phase has a potential difference of 220 volts relative to the neutral wire.

 What is a neutral wire or conductor?
What is a neutral wire or conductor?
The neutral wire is one of the most important wires in the city's electricity supply system, which poses no danger to the public and can be touched without being electrocuted. As mentioned, the electric current is not established until there is a return path to the source. The neutral wire is actually the wire that is used to make this circuit or the closed path, and it actually returns the output current from the electrical device to the generator. The neutral wire is usually identifiable by the blue insulator.

 What is earth wire or earth conductor?
What is earth wire or earth conductor?
Most electrical appliances have a metal body. Since metals are conductors of electricity, there is always a risk that they will be electrified. To solve this problem and prevent possible problems, the earthing system in the building and all the equipment with metal body are used. To protect people, when working with electrical appliances, the body of the device is usually connected with a wire to the water pipe, where the water pipe is in contact with the wet parts of the ground. This wire is called earth wire. In fact, this wire must also be connected to the earth well, but to save it, it is connected to the water pipe. The wire is insulated with green-yellow paints.

 What is the difference between neutral and earth wires?
What is the difference between neutral and earth wires?
If electricity comes into contact with the body for any reason, the fuse will go out because the earth wire with resistance will transmit all the current entering the house to the ground. That is, all of a sudden, a strong current passes through the fuse and the fuse blows. Earthing wire is only used for extra protection. Its existence is not necessary, while the existence of zero is necessary. In most countries, ground wire is included in the circuit when wiring. So instead of two branches, they use three branches, one of which is the earth wire.


 What is the difference between single-wire and multi-wire
electrical wires?
What is the difference between single-wire and multi-wire
electrical wires?
■ Multi-threaded electric wire, no matter how thick, is still more flexible than wired wire. Where wiring needs to be manipulated and soldered, it is more commonly used, such as electronic circuits.
■ Multi-core electric wire is more resistant to the fatigue phenomenon of materials and wire mesh is less used when this phenomenon is problematic. The phenomenon of material fatigue is caused by the passage of time and climate change, and as a result, changes in the structure of the material, which causes fractures and small cracks in the metal, which later become larger and the metal or conductor of the electrical wire breaks.
■ The cost of producing multi-stranded electric wires is higher than that of electric wires, and they use wire when the number of wires used is high and requires less flexibility.
■ Wired wires are also used in applications other than electronics and electricity, although they are rare, but in mechanics they use wired wires to move or secure something.
■ The electrical resistance of a multi-stranded wire is greater than that of a single-stranded wire, because the cross-sectional area of a multi-stranded wire increases despite the gaps between the strands.
■ Multi-threaded wire is more commonly used at high frequencies, why? Because there is a phenomenon called skin effect, or Skin Effect in wires, which causes a loss of power in the wire. Of course, ordinary multi-threaded wires do not greatly reduce the skin effect, and to reduce this effect, they use a multi-threaded cable called Litz or Litz Cable. Litz cables are actually multi-threaded wires that are insulated from each other with insulating coating and increase the overall cross-sectional area for current flow.
Posts related to Electric Wire - Conductors used in Electric Wire - Color Electric Wire
All material and intellectual rights are reserved for the NiruTavan